History

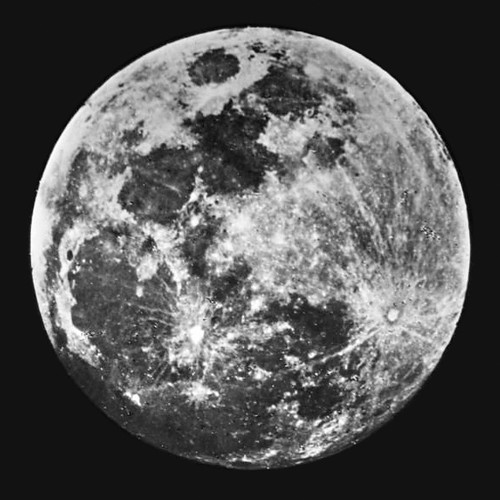
In 1840, John William Draper, an American physicist, took the first photograph of the Moon using a technique called daguerreotype. This technique involved exposing a light-sensitive silver plate to mercury vapor. The resulting photograph of the Moon was rudimentary in terms of details, but it marked the beginning of space photography, becoming a significant advancement in the field of astrophotography.


.jpg)
Warren De la Rue, a British astronomer, played a crucial role in the early days of astrophotography. In 1851, he used photography to document a total solar eclipse, marking the beginning of solar photography. De la Rue designed a special telescope equipped with a camera to capture the solar eclipse, which allowed scientists to study the solar atmosphere and phenomena like prominences and the solar corona.
These early attempts in astrophotography were pivotal steps, even though the photographic techniques of the time were slow and not very light-sensitive, limiting the quality of astronomical images. Despite these challenges, these pioneers paved the way for an exciting era of discoveries by enabling astronomers to visually record and share their observations of the night sky.

In the late 19th century, astrophotography underwent a significant evolution with the adoption of light-sensitive photographic plates. This transition allowed for longer exposures and more detailed astronomical images, opening new avenues in the study of the universe.
Photographic plates, which were glass or glass-coated supports coated with photosensitive materials like silver gelatin emulsion, proved to be much more light-sensitive than the metal plates previously used. This meant that astronomers could expose these plates for longer periods to capture sharper images of the night sky.
Edward Emerson Barnard, an American astronomer, was one of the key figures of this era. He used photographic plates to make significant discoveries, including the finding of numerous double stars and the detection of Jupiter's fifth moon, Amalthea. Barnard was renowned for his patience and expertise in long-exposure astrophotography, which allowed him to capture more detailed images of celestial objects.

Isaac Roberts, a British amateur astronomer, also made significant contributions to astrophotography during this time. He dedicated a lot of time to photographing nebulae and galaxies. In 1893, he published a catalog of deep-sky object photographs, aiding the advancement of extragalactic astronomy. His images of the Andromeda Galaxy were particularly remarkable for their time.
The adoption of photographic plates allowed astronomers to produce astronomical images of unprecedented quality, revealing new details and celestial objects. This paved the way for important discoveries in the field of astronomy, expanding our understanding of the universe beyond our solar system. The transition to plate photography marked a crucial milestone in the history of astrophotography.
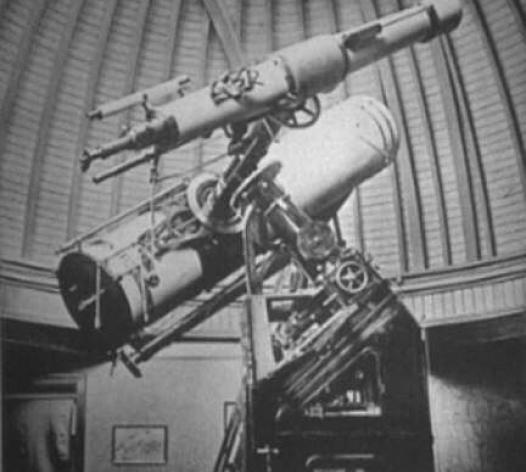



George Ritchey, an American astronomer and optical engineer, collaborated with Henri Chrétien, a French astronomer and inventor, to develop the Ritchey-Chrétien telescope in the early 20th century. This telescope, known for its advanced optical design, was ideally suited for astrophotography. Its optical system eliminated optical aberrations, producing sharper images on photographic plates. The Ritchey-Chrétien telescope is still widely used today for professional astrophotography and research projects.George Ritchey, un astronome et ingénieur optique américain, a collaboré avec Henri Chrétien, un astronome et inventeur français, pour développer le télescope de Ritchey-Chrétien au début du XXe siècle. Ce télescope, caractérisé par sa conception optique avancée, était idéalement adapté à l'astrophotographie. Son système optique éliminait les aberrations optiques, ce qui produisait des images plus nettes sur les plaques photographiques. Le télescope de Ritchey-Chrétien est encore largement utilisé aujourd'hui pour des projets d'astrophotographie professionnelle et de recherche.


George Ellery Hale was an American astronomer who had a major impact on solar astrophotography. He designed the Hale Solar Telescope, an exceptionally powerful instrument dedicated to studying the Sun. This telescope was equipped with a special camera to capture images of the Sun in visible light and H-alpha light (a spectral line of hydrogen). The images from the Hale Solar Telescope revolutionized our understanding of the Sun, enabling detailed observations of sunspots, solar prominences, and other dynamic solar phenomena.
The advent of specialized photographic telescopes allowed astronomers to make significant progress in understanding the universe, whether by observing distant celestial objects or studying our own star, the Sun. These advancements also opened new opportunities for astrophotography, enabling astronomers to explore the universe with precision and depth never before achievable.

Starting from the late 20th century, astrophotography underwent a radical transformation thanks to the advent of digital technology. This era brought about significant changes in how astronomers captured and utilized astronomical images.
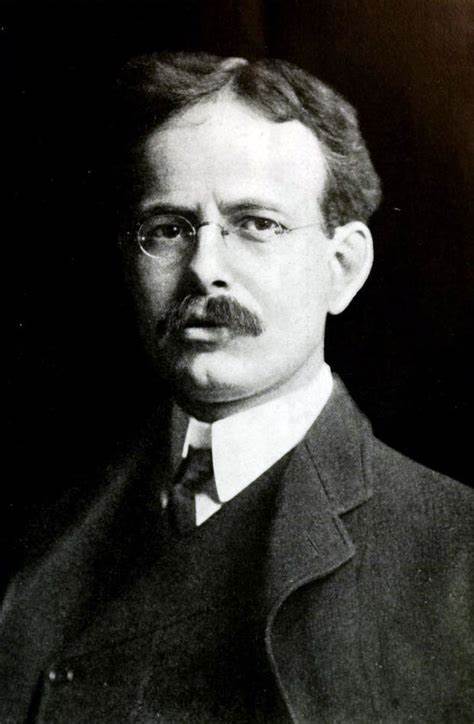
One of the most significant advancements in astrophotography was the introduction of Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) cameras in the 1970s and 1980s. CCDs are photosensitive sensors capable of recording digital images with high light sensitivity. They radically improved the quality of astronomical images by enabling longer exposures without a loss of quality.
A. Delano, an engineer at Texas Instruments, played a key role in the development of the first CCD cameras specifically designed for astronomy. These cameras were quickly embraced by the astronomical community and became an essential tool in astrophotography.

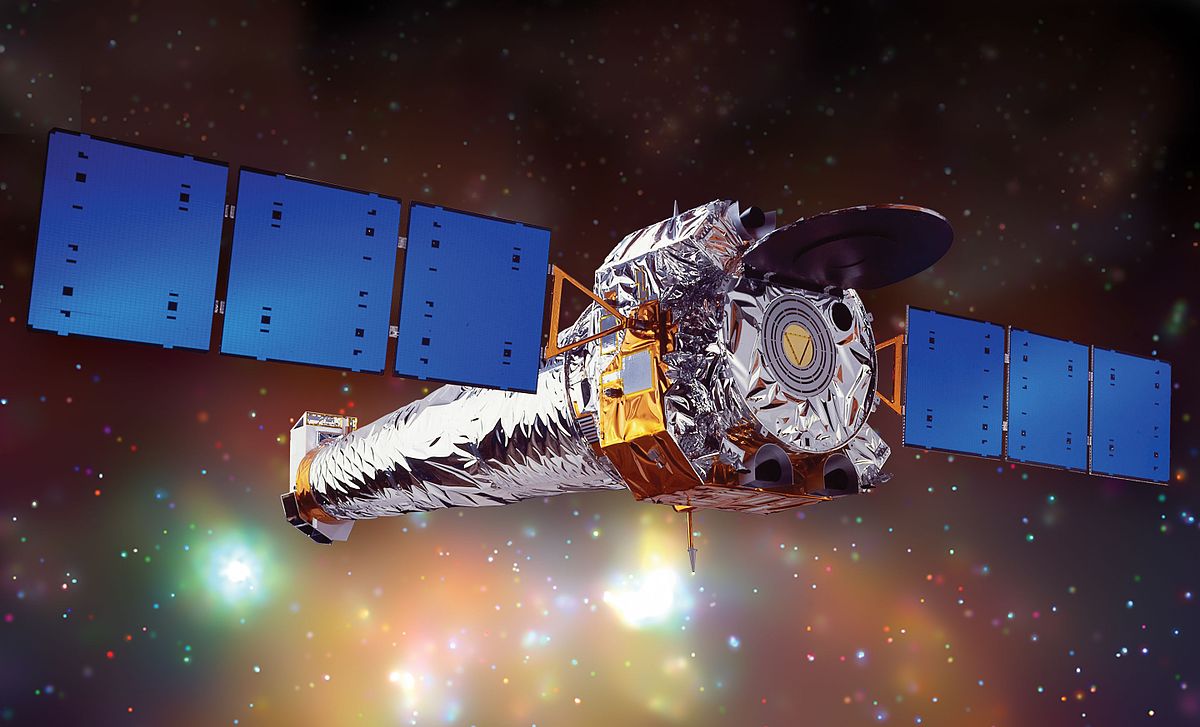
During this period, space telescopes became major players in astrophotography. The Hubble Space Telescope, launched in 1990, is perhaps the most famous among them. Equipped with an advanced CCD camera, Hubble captured spectacular images of the distant universe, revolutionizing our understanding of astronomy. Other space telescopes, such as Chandra (X-rays), Spitzer (infrared), and Kepler (exoplanet detection), also made significant contributions to astrophotography.
This digital era allowed astronomers to obtain astronomical images of unparalleled quality. Digital images could be quickly processed, enhanced, and shared with the scientific community and the general public. Furthermore, the use of astrophotography in education and popularizing astronomy became common, helping to spark public interest in the universe and share the beauty of the cosmos.



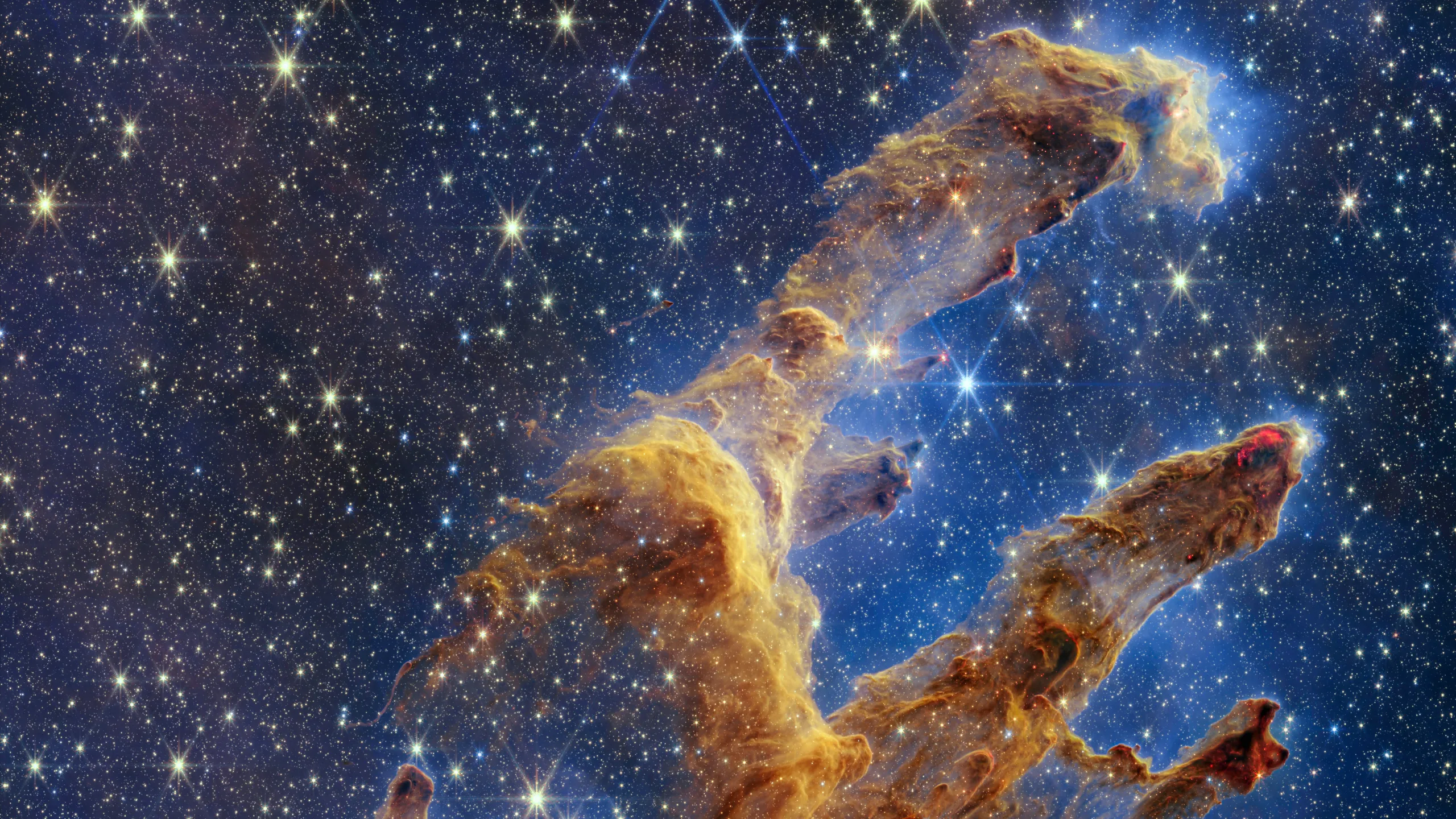
The JWST is a revolutionary space telescope named in honor of James E. Webb, who served as the NASA administrator from 1961 to 1968 and played a crucial role in the Apollo program. The JWST is an international project led by NASA in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The James Webb Telescope is the most ambitious and complex space observatory ever constructed, and its images are truly breathtaking.